- products
- Science
- wellness journal
- About Us
- Faqs
- Sustainability
- Contact Us
- Self Test
- English

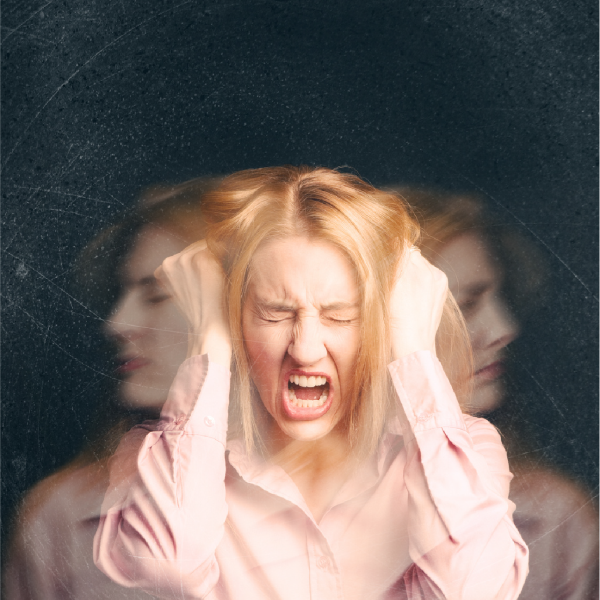
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder affecting millions of women worldwide. While often associated with irregular periods, excessive hair growth, acne, and weight gain, one of the less discussed but equally significant impacts of PCOS is “its effect on sexual health”.
PCOS’s impact on sexual health is multifaceted, affecting physical, emotional, and psychological well-being. Understanding the connection between PCOS and sexual health is vital for women’s overall well-being.
Understanding PCOS
PCOS can be identified by the presence of two out of three criteria:
1. Irregular or absent menstrual cycles (oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea),
2. Polycystic ovarian morphology (the presence of multiple cysts on the ovaries), and
3. Hyperandrogenism (excess male hormones),
Hormonal Imbalance and Its Effects
“At the core of PCOS lies a hormonal imbalance.” The ovaries produce excessive amounts of androgens, male sex hormones, which can manifest in various physical symptoms such as
1. Hirsutism (excess body hair),
2. Hair thinning or hair loss from the scalp,
3. Oily skin, acne, and weight gain,
4. Skin tags
5. Darkening of the skin – particularly along neck creases, in the groin, and underneath the breasts.
Additionally, PCOS is associated with an increased risk of developing insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and infertility (difficulty in conceiving due to irregular ovulation).
However, one aspect that often goes unnoticed is how PCOS affects a woman’s sexual health.
PCOS & Sexual Health: An Over-looked Connection
The hormonal fluctuations experienced by women with PCOS can significantly impact sexual health. Elevated androgen levels can lead to decreased libido, affecting sexual desire and arousal. A study (1) indicated that nearly 60% of women with PCOS reported low sexual arousal or desire, which can lead to a diminished quality of life and increased feelings of depression and anxiety.
Moreover, the psychological effects of PCOS, including body image issues stemming from symptoms like hirsutism and acne, can further exacerbate sexual dysfunction. Women may feel less attractive or confident, leading to a reluctance to engage in sexual activity. This emotional burden can create a cycle where low sexual desire leads to relationship difficulties, which in turn can worsen self-esteem and mental health.
Impact of PCOS on Sexual Health:
1. Reduced Libido: Women with PCOS often report a decrease in sexual desire. This can be attributed to hormonal imbalances, particularly elevated levels of androgens and insulin resistance (2).
Elevated androgen levels can disrupt the normal hormonal balance needed for a healthy sexual desire. Insulin resistance, further complicates this by contributing to energy fluctuations and overall fatigue, reducing sexual interest and enthusiasm. This makes sex, less enjoyable and infrequent.
2.Vaginal Dryness: Hormonal fluctuations (particularly lower levels of estrogen) can affect vaginal lubrication, leading to dryness and discomfort during intercourse. This can make sexual activity painful and reduce overall sexual satisfaction. This symptom is often exacerbated by anxiety and stress related to sexual performance and body image concerns, leading to a reduction in sexual activity.
3.Painful Intercourse: Women with vaginal dryness and other PCOS-related symptoms can cause dyspareunia, or painful intercourse, particularly if they have endometriosis or pelvic adhesions. This can further diminish sexual desire and lead to avoidance of sexual activity creating a negative feedback loop that further diminishes sexual satisfaction.
4. Orgasm and Satisfaction: The ability to achieve orgasm can also be affected in women with PCOS. Studies (3) suggest that the hormonal environment created by PCOS may impair the physiological responses necessary for orgasm, leading to lower overall sexual satisfaction.
5. Body Image Issues: Symptoms like weight gain, acne, and excessive hair growth can negatively impact body image and self-esteem. Women with PCOS may feel less attractive or confident, which can, in turn, affect their sexual relationships.
6. Emotional factors: The physical and emotional challenges of PCOS can contribute to feelings of stress, anxiety, and depression. These conditions can further exacerbate sexual dysfunction by reducing libido and increasing stress levels. Anxiety, in particular, can lead to performance-related concerns, making sexual activities feel more like a source of stress than pleasure.
7. Infertility and Its Psychological Impact: The challenges of infertility, a common concern for women with PCOS, can also have a profound impact on sexual health. The emotional toll of trying to conceive, coupled with repeated disappointments, can make sex feel more like a chore than an act of intimacy and connection. This shift in perception can diminish sexual pleasure and satisfaction, leading to a cycle of reduced libido and avoidance of sexual activity.
8. Relationship Dynamics: PCOS-related sexual health issues can put a strain on romantic relationships. Partners may experience feelings of confusion or rejection, attributing a decrease in intimacy to a lack of interest. This can lead to emotional distance. Open communication about PCOS and its effects is essential, but many women find it challenging to discuss their struggles, further exacerbating relationship stress.
Break the Silence:
PCOS’s impact on sexual health is often overlooked. It’s essential to address these concerns, promote awareness, and encourage open conversations. Women with PCOS deserve comprehensive care, addressing physical, emotional, and psychological aspects.
Addressing Sexual Health Issues in PCOS
Managing the sexual health issues associated with PCOS requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of the condition.
1. Lifestyle Changes:
While PCOS is a hormonal disorder, lifestyle factors can also play a role in managing symptoms and improving sexual health. These factors include:
● Healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet can help regulate hormones and support overall health.
● Regular exercise: Physical activity can help with weight management and improve insulin sensitivity and reduce androgen levels, which may help alleviate sexual health issues.
● Stress management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help reduce stress and anxiety.
● Adequate sleep: Getting enough sleep is essential for overall health and well-being.
2. Psychological Support: Counseling or therapy can be beneficial for women dealing with the emotional and psychological impacts of PCOS. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) has been shown to be effective in managing anxiety and depression associated with PCOS.
3. Communication: Open communication with a partner about sexual health issues is crucial and will help in alleviating some of the emotional strain. Understanding and support from a partner can help reduce anxiety. Supportive relationships can foster a better understanding of the condition, which may improve intimacy and sexual satisfaction.
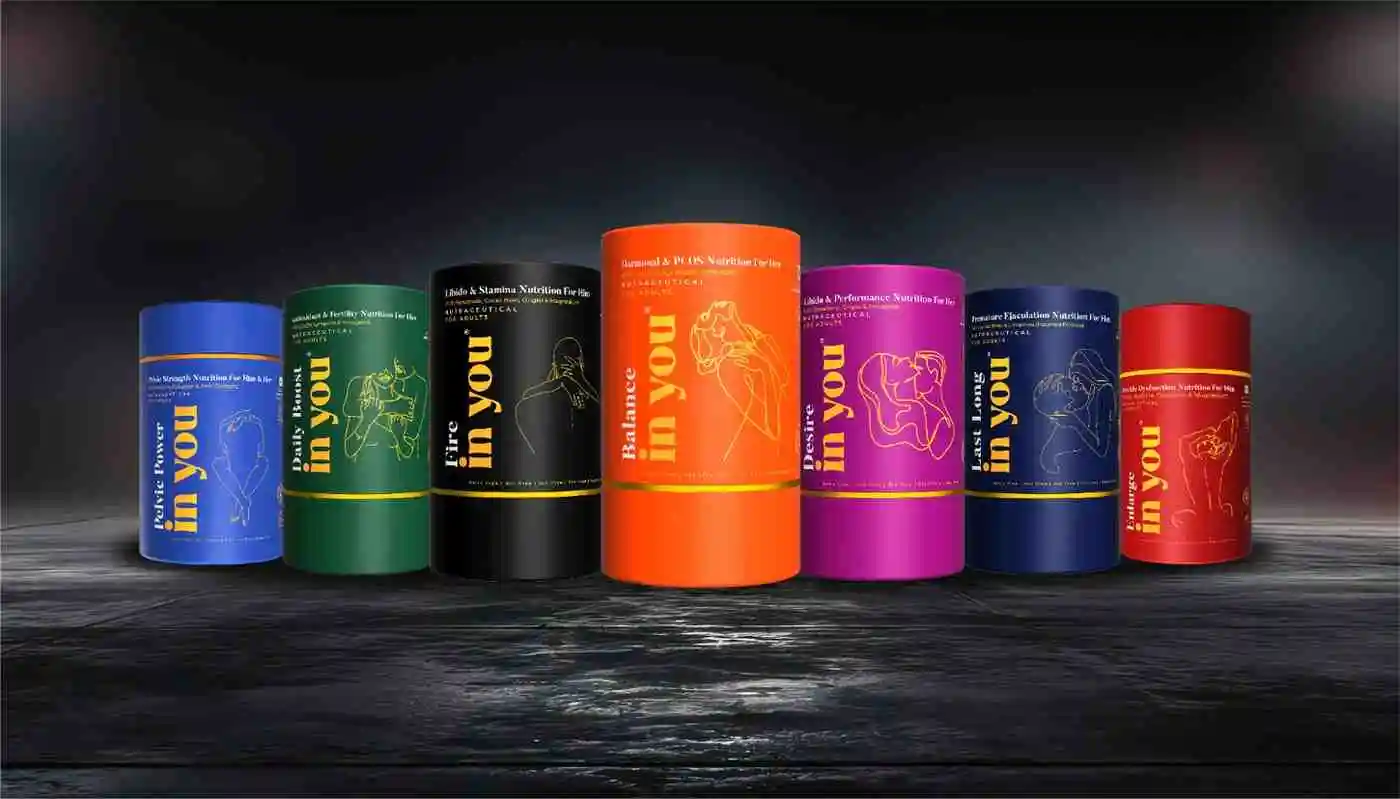
4. Nutritional Interventions: Targeted supplements can help balance hormones, improve mood, and alleviate some of the physical symptoms that negatively impact sexual health.Some of them include:
Chaste berry extract (4): It helps to balance the levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and prolactin, thereby improving the balance of estrogen and progesterone.
Fenugreek extract: It is known for its potential in improving insulin sensitivity, it helps combat weight gain and improve energy levels, enhancing libido and sexual satisfaction.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10): It supports PCOS management by enhancing insulin sensitivity, boosting mitochondrial function, and improving egg quality. Its antioxidant properties help reduce oxidative stress, promote regular ovulation, and support overall reproductive health in women with PCOS.
Other ingredients such as Myo-inositol, Alpha Lipoic Acid, Chromium picolinate, Zinc citrate, Vitamins B6, B9, and B12 act synergistically and help in alleviating the symptoms of PCOS.
While it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements, certain nutrients may play a role in balancing hormones and addressing symptoms of PCOS.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is a complex condition that can significantly impact a woman’s sexual health. The interplay of hormonal imbalances, psychological factors, and relationship dynamics creates a challenging environment for many women. However, with appropriate medical treatment, psychological support, and lifestyle changes, it is possible to manage the symptoms of PCOS and improve sexual health.
By understanding the relationship between PCOS and sexual health, and by seeking appropriate treatment and support, women can improve their quality of life and enhance their sexual well-being. While lifestyle changes and medical interventions play a crucial role, nutraceuticals may offer a valuable complementary approach to managing PCOS and its associated symptoms.
Author:

Dr. Indraneel
Medical Writer
|Source:
1. Texas Healthcare OBGYN. (n.d.). Can PCOS cause low sex drive? Treatment options for low libido. Retrieved from https://mytexashealthcareobgyn.com/well-woman-care/can-pcos-cause-low-sex-drive-treatment-options-for-low-libido/
2. Ross, C. (2023, June 2). What to do if PCOS symptoms are impacting your sex life. Mashable. Retrieved from https://in.mashable.com/sex-dating-relationships/53877/what-to-do-if-pcos-symptoms-are-impacting-your-sex-life
3. Pastoor, H., Both, S., Laan, E. T. M., & Laven, J. S. E. (2023). Sexual dysfunction in women with PCOS: A case control study. Human Reproduction, 38(11), 2230-2238. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/dead193
4. Okell, A. (2023, July 30). Vitex for PCOS: Does agnus castus (chasteberry) help PCOS? PCOS Collective. Retrieved from https://pcoscollective.com/vitex-for-pcos/

Dr. Indraneel
Medical Writer
|A health and wellness blogger with a passion for empowering people through informed choices. He combines his expertise in science and healthcare to offer insights that promotes better well-being. Outside of writing, he is a cricket enthusiast and an avid reader.


Embrace your body, ignite intimacy, and unlock boundless pleasure.
Related Products

Get 10% off
on your first order
You’ll also get dibs and a heads up on any sales or product launches.